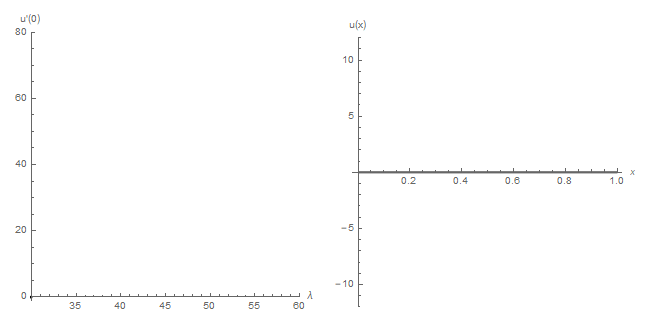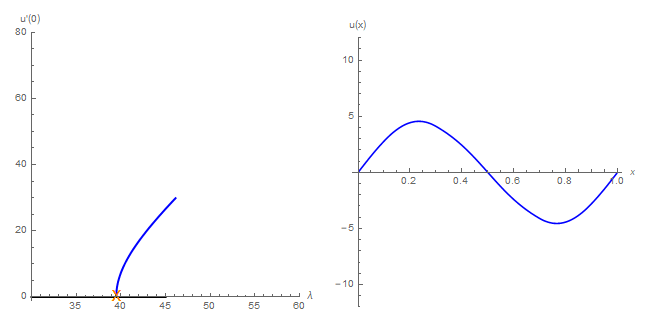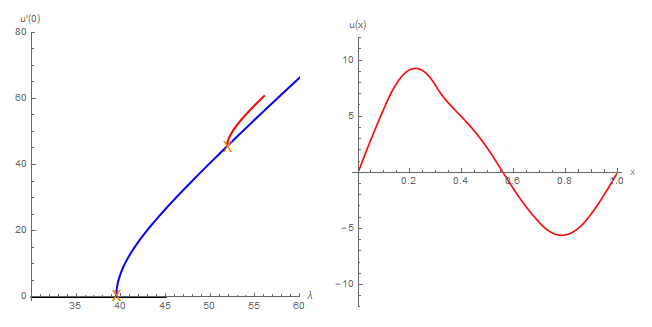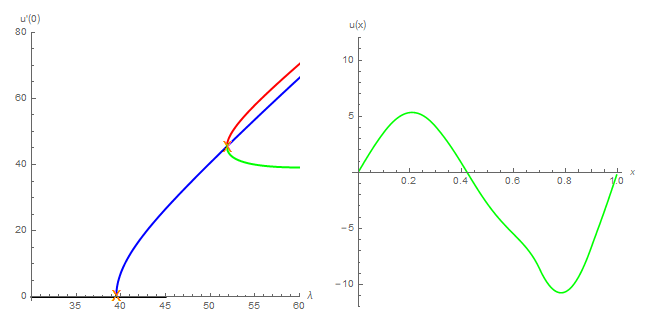
 Reaction-diffusion equations can be used to describe the spatial and temporal evolution of one or several species in a certain habitat. Ascertaining the number of steady states and their qualitative properties is one of the starting point in the analysis of such models. This amounts to solve the elliptic counterpart of the reaction-diffusion equations.
In this research line, a particular emphasis is given to the influence of heterogeneities of the habitat on the number of solutions. A high multiplicity of steady states, indeed, may be a signal of complex dynamics in the associated problem with time dependence.
In particular, the considered heterogeneities model the coexistence of regions where the individuals of the species compete among themselves in some parts, according to the classical logistic model, but cooperate in others.
The involved methods are: phase-plane techniques and topological methods, sub- and supersolutions, continuation and bifurcation methods.
The main obtained novelties are related to the existence of a large number of solutions for some ranges of the parameters.
The analytical study is complemented by numerical simulations, which, in some cases, has required the refinement of the available numerical continuation methods.
Reaction-diffusion equations can be used to describe the spatial and temporal evolution of one or several species in a certain habitat. Ascertaining the number of steady states and their qualitative properties is one of the starting point in the analysis of such models. This amounts to solve the elliptic counterpart of the reaction-diffusion equations.
In this research line, a particular emphasis is given to the influence of heterogeneities of the habitat on the number of solutions. A high multiplicity of steady states, indeed, may be a signal of complex dynamics in the associated problem with time dependence.
In particular, the considered heterogeneities model the coexistence of regions where the individuals of the species compete among themselves in some parts, according to the classical logistic model, but cooperate in others.
The involved methods are: phase-plane techniques and topological methods, sub- and supersolutions, continuation and bifurcation methods.
The main obtained novelties are related to the existence of a large number of solutions for some ranges of the parameters.
The analytical study is complemented by numerical simulations, which, in some cases, has required the refinement of the available numerical continuation methods.
Involved professors
- Andrea Tellini (in collaboration with the research groups Eliparanoli and Deg1)
Recent publications
- A. Tellini, Numerical global bifurcation diagrams for a superlinear indefinite problem with a parameter appearing in the domain, Rendiconti dell’Istituto di Matematica dell’Università di Trieste, 52, 2020.
- A. Tellini, High multiplicity of positive solutions for superlinear indefinite problems with homogeneous Neumann boundary conditions, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 673-698, 2018
Profesores involucrados
Publicaciones recientes
- Cilia, R, Gutiérrez J. M. Universal mappings for certain classes of operators and polynomials between Banach spaces, Math. Nachr, vol. 290, 2788–2799, 2017.
- Cilia, R, Gutiérrez J. M. Polynomials with an integral representation, J. Math. Anal. Appl, vol. 455, 246–262, 2017.
- Cilia, R, Gutiérrez J. M. Nonexistence of certain universal polynomials between Banach spaces, J. Math. Anal. Appl. vol. 427, 962–976, 2015.
- Cilia, R, Gutiérrez J. M. Asplund operators and p-integral polynomials, Medit. J. Math, vol. 10, 1433–1457, 2013.
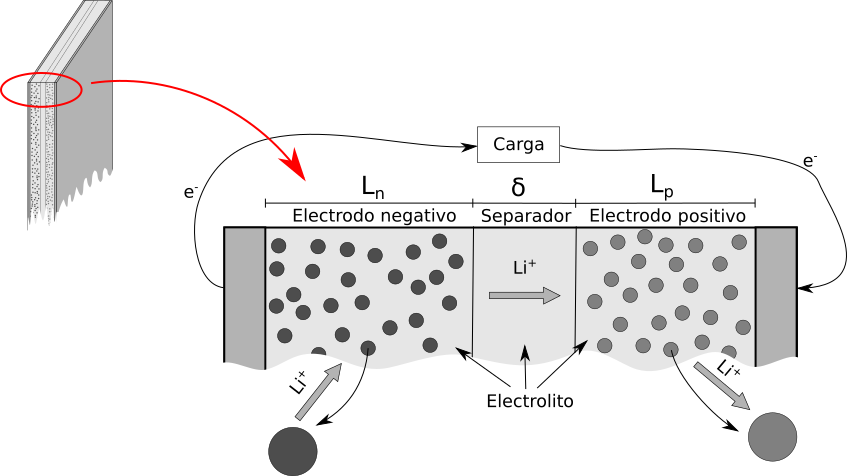
Las baterías para el almacenamiento de energía eléctrica están presentes en gran cantidad de dispositivos de nuestro día a día: teléfonos móviles, ordenadores portátiles, cámaras, vehículos de movilidad urbana (patinetes, bicicletas, etc) y, por supuesto, el coche eléctrico. De hecho, la implantación de muchos de estos dispositivos en nuestra vida cotidiana está estrechamente ligada al desarrollo que las baterías han tenido en los últimos años. Hay distintos tipos de baterías pero, a día de hoy, las que han mostrado mejores prestaciones son las baterías de ion Litio.
En general, la mejora en el diseño de las baterías pasa por la realización de ensayos para estudiar qué configuración proporciona el comportamiento más eficiente. La fabricación de baterías es un proceso costoso y que genera grandes cantidades de residuos. Entender bien los mecanismos que tienen lugar en la batería puede ayudar a mejorar su diseño. Para ello una de las herramientas más potentes es la de la modelización físico-matemática. En efecto, estos modelos permiten simular aspectos cuantitativos de su comportamiento sin la necesidad de fabricarlas y de llevar a cabo los ensayos, con el ahorro de tiempo y dinero que esto conlleva. En particular, se puede estudiar cómo afectan al comportamiento de la batería (densidad de energía, envejecimiento, etc) aspectos tales como, por ejemplo, las dimensiones de la celda o los materiales empleados en su diseño.
Entre los distintos tipos de modelos para baterías de ion de litio, están los denominados modelos electroquı́micos multifı́sicos, que proporcionan una descripción completa de los mecanismos internos de la baterı́a a escala macroscópica sin ser tan exigentes computacionalmente como los modelos a escala microscópica. Es en este campo en el que están involucrados los investigadores de esta línea, en concreto en el desarrollo y análisis de modelos matemáticos y numéricos de los denominados modelos micro-macro. Estos modelos acoplan una serie de Ecuaciones en Derivadas Parciales que se discretizan mediante una combinación adecuada entre el método de Elementos Finitos y esquemas Runge-Kutta-Chebyshev.
Profesores involucrados
- Rodolfo Bermejo
- Pedro Galán del Sastre
- Luis Sanz Lorenzo
- Alejandro Zarzo Altarejos
- Víctor Muñoz Villarragut
Publicaciones recientes
- Bermejo, R., Galán del Sastre, P. An implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta-Chebyshev finit element method for the nonlinear Lithium-ion battery equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, vol. 361, 398-420, 2019.
El estudio de la dinámica de un fluido es un problema extremadamente complicado pero que sin embargo es de vital importancia en numerosos campos dentro de la industria como del medio ambiente. A día de hoy dar respuesta a los numerosos problemas que necesitan del conocimiento preciso de ciertos flujos pasa por la resolución numérica de un conjunto de Ecuaciones en Derivadas Parciales, donde las ecuaciones de Navier-Stokes son el punto de partida.
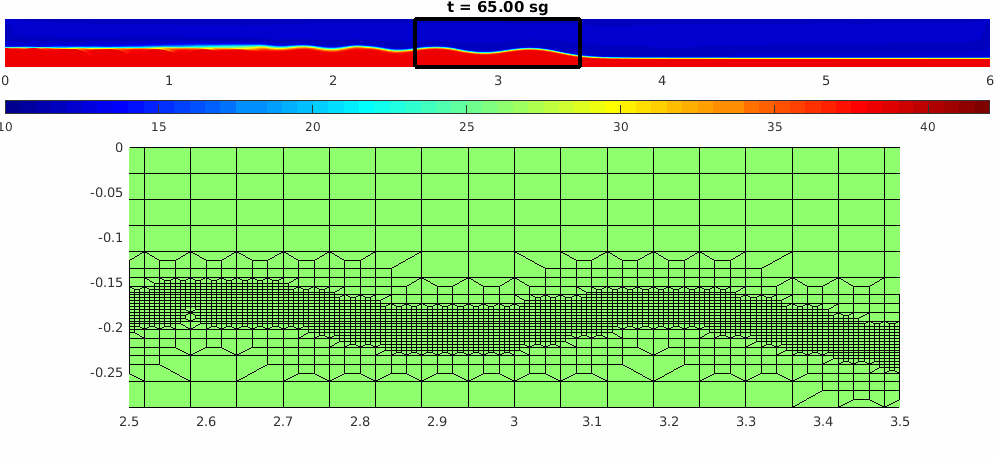
Los investigadores responsables de esta línea de investigación han centrado parte de su carrera investigadora en el desarrollo de esquemas numéricos para resolver distintas aplicaciones relacionadas con la mecánica de fluidos entre las que cabe destacar: procesos de combustión «spray», problemas de interfase, ecuaciones para el estudio de la circulación general del océano.
Los métodos numéricos desarrollados se han centrado en el método de Elementos Finitos conforme y han explorado diversas técnicas numéricas como: métodos de Lagrange-Galerkin, adaptación en espacio y tiempo, esquemas level-set, elementos finitos hp de alto orden vs bajo orden, etc.
Profesores involucrados
- Rodolfo Bermejo
- Pedro Galán del Sastre
- Laura Saavedra (Departamento de Matemática Aplicada a la Ingeniería Aeroespacial, E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos)
- Jaime Carpio (Departamento de Ingeniería Energética)
- Juan Luis Prieto (Departamento de Ingeniería Energética)
Publicaciones recientes
- Carpio, J., Prieto, J.L., Galán del Sastre, P. An anisotropic adaptive, Lagrange-Galerkin numerical method for spray combustion. Journal of Computational Physics, vol. 381, 246-274, 2019.
- Galán del Sastre, P., Bermejo, R. A Lagrange-Galerkin hp-Finite Element Method for a 3D Nonhydrostatic Ocean Model. Pure and Applied Geophysics, vol. 173 (3), 885-907, 2016.
- Bermejo, R. Saavedra, L. Lagrange-Galerkin methods for incompressible Navier-Stokes equations: a review. Communications in Industrial and Applied Mathematics, vol. 7, 26-55, 2016.
- Bermejo, R., Saavedra, L. Modified Lagrange-Galerkin methods to integrate time dependent incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput., vol. 37, B779-B803, 2015.
- Bermejo, R., Galán del Sastre, P., Saavedra, L. A subgrid viscosity Lagrange-Galerkin method for convection-diffusion problems. International Journal of Numerical Analysis and Modeling, vol. 11 (2), 288-302, 2014.
.
Se ofertan tesis doctorales, TFM, TFG.
Profesores involucrados
- Jesús San Martín Moreno
- María José Moscoso Castro
- Dolores Sotelo Herrera
- Mª Carmen García-Miguel Fernández
- Olga Velasco Manuel
Publicaciones recientes
- Herrera, M. D. S., San Martin, J., Porter, M. A. Heterogeneous, weakly coupled map lattices. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, vol. 36, 549-563, 2016
- Martín, J. S., Gómez, A. G., Moscoso, M. J., Rodríguez-Pérez, D. Compound orbits break-up in constituents: an algorithm, 2014.
- Martín, J. S., Porter, M. A. Convergence Time towards Periodic Orbits in Discrete Dynamical Systems. PLOS ONE, vol. 9 (4), 1-9, 2014.
- Martín, J. S., O’Farrell, A. G. A general stability criterion for switched linear systems having stable and unstable subsystems. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, vol. 27 (11), 1000-1011, 2013.
- Sotelo Herrera, M. D., San Martin, J., Cerrada, L. Saddle-Node Bifurcation Cascades and Associated Traveling Waves in Weakly Coupling Cml. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, vol. 22 (7), 1250172, 2012.
Profesores involucrados
Publicaciones recientes
- González-Guillén, C. E., Jimenez, C. H., Palazuelos, C., Villanueva, I. Sampling quantum non-local correlations with high-probability, Communications in Mathematical Physics, vol. 344 (1), 2016.
- González-Guillén, C. E., Palazuelos, C., Villanueva, I. Euclidean Distance between Haar Unitary and Random Gaussian Matrices, Journal of Theoretical Probability, 2016.
- Collins, B., González-Guillén, C. E., Pérez-García, D. Matrix product states, random matrix theory and the principle of maximum entropy, Communications in Mathematical Physics, vol. 320 (3), 2013.
- González-Guillén, C. E., Multipartite maximally entangled states in symmetric scenarios, Phys. Rev. A, vol. 86 (2), 022304, 2012.
- A. Usui, A. Sanpera, and M. G. Díaz, ‘Simplifying the simulation of local Hamiltonian dynamics’, Phys. Rev. Res., vol. 6, p. 023243, Jun. 2024.
- C. Marconi, P. C. Saus, M. G. Díaz, and A. Sanpera, ‘The role of coherence theory in attractor quantum neural networks’, Quantum, vol. 6, p. 794, Sep. 2022.
- M. G. Díaz, G. Sentís, R. M. Tapia, and A. Sanpera, ‘Volumes of parent Hamiltonians for benchmarking quantum simulators’, Phys. Rev. Res., vol. 4, p. 023228, Jun. 2022.
- P. Strasberg, M. G. Díaz, and A. Riera-Campeny, ‘Clausius inequality for finite baths reveals universal efficiency improvements’, Phys. Rev. E, vol. 104, p. L022103, Aug. 2021.
Profesores involucrados
- Mª Elena Domínguez
- Nuria González Prelcic (Universidad de Vigo)
Publicaciones recientes
- Domínguez Jiménez, M. E., González Prelcic, N., Vazquez-Vilar, G., LópezValcarce, R. Design of universal multicoset sampling patterns for compressed sensing of multiband sparse signals, Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2012), 3337-3340. Kioto, Japan, Marzo de 2012.
- Domínguez Jiménez, M. E., González Prelcic, N. Analysis and Design of Multirate Synchronous Sampling Schemes for Sparse Multiband Signals, Proceedings of the 20th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2012), 1184-1188. Bucarest, Romania, Agosto de 2012.
- González Prelcic, N., Domínguez Jiménez, M.E. Circular sparse rulers based on co-prime sampling for compressive power spectrum estimation, Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM 2014), Austin, Texas, USA. Diciembre de 2014.
Reaction-diffusion equations can be used to describe the spatial and temporal evolution of one or several species in a certain habitat. Some basic questions that arise, if the species is initially located in a bounded region of the domain, are whether it can eventually invade the whole domain, and – if so – at what speed.
In this research line, such questions are analyzed in the context of the presence of one or several regions in the domain where the individuals disperse faster than in the others. This is the case for example of the tiger mosquitos (aedes albopictus), which are transported by trucks on highways and of the yellow legged hornet (vespa velutina) which is known to spread faster along waterways like rivers.
 The involved methods rely on comparison principles and the study of eigenvalue problems.
The involved methods rely on comparison principles and the study of eigenvalue problems.
The main results are related to the characterization of the propagation speed and the study on how it depends on the several parameters of the model. A particular emphasis is given to the cases in which the propagation can be stopped or, on the contrary, enhanced by the presence of the heterogeneities.
Involved professors
- Andrea Tellini (in collaboration with the international research group ReaDi)
Recent publications
- B. Bogosel, T. Giletti, A. Tellini, Propagation for KPP bulk-surface systems in general cylindrical domains, preprint.
- H. Berestycki, L. Rossi, A. Tellini, Coupled reaction-diffusion equations on adjacent domains, preprint.
- A. Tellini, Comparison among several planar Fisher-KPP road-field systems, Chapter in “Contemporary Research in Elliptic PDEs and Related Topics”, Springer INdAM Series, 2019.
Profesores involucrados
Profesores involucrados
Publicaciones recientes
- Casanova, M. S. On some families of links and new approaches to link homologies, 2015
- Michelena, L. E. PROYECTO FIN DE CARRERA Optimización topológica de dispositivos mezcladores, 2012
Profesores involucrados
- Mª Elena Domínguez
- Gabriela Sansigre
- David Luengo García (Departamento de Teoría de la Señal y Comunicaciones, E.T.S. Ingeniería y Sistemas de Telecomunicación, UPM)
- Fernando Cruz Roldán (Universidad de Alcalá)
Publicaciones recientes
- Cruz-Roldán, F., Domínguez-Jiménez, M.E., Sansigre-Vidal, G., Amo-López, P., Blanco-Velasco, M., Bravo-Santos, Á. On the Use of Discrete Cosine Transforms for Multicarrier Communications, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, vol. 60 (11), 6085-6090, 2012.
- Cruz-Roldán, F., Domínguez-Jiménez, M.E., Sansigre-Vidal, G., Piñeiro-Ave, J., Blanco-Velasco, M. Single-Carrier and Multicarrier Transceivers based on Discrete Cosine Transform Type-IV, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, vol. 12 (12), 6454-6463, 2013.
- Cruz-Roldán, F., Domínguez-Jiménez, M. E., Sansigre-Vidal, G., Luengo, D., Moonen, M. DCT-based channel estimation for single and multicarrier communications. SIGNAL PROCESSING, vol. 128, 332 339, 2016.
Profesores involucrados
Publicaciones recientes
- Casanova, M. S. On some families of links and new approaches to link homologies, 2015
- Michelena, L. E. PROYECTO FIN DE CARRERA Optimización topológica de dispositivos mezcladores, 2012



